As you may know the Korean economy is largely dominated by conglomerates like Samsung, SK, Hyundai and LG. One study even finds that “31 chaebols control 2/3 of facilities investment and exports”. One the one hand you have huge corporations, on the other hand you have a great amount of businesses like convenience stores, coffee shops, chicken restaurants and taxi drivers (with less than 5 employees). There is not much in between. Korea is not known for its “mittelstand” or small and medium sized enterprises. The Korean government is trying to change that. It will “infuse 12 trillion won (US$12 billion) in the system by 2022.” It is funding startups (companies with a scalable business model) and even made a “Ministry of startups”. Korea is already home to unicorns like Coupang, Woowa Brothers and Toss. Will the government help grow more Korean unicorns?

Left: startups
Right: to be disrupted industries
Copyright: Lucas Film
This blog post consists of the following parts:
- What is a startup ecosystem?
- Incubation centers / accelerators in Seoul and Pangyo
- Co-working spaces in Seoul
- Korean startup jobs
- Korean unicorns
- Korean technology and innovation
- Conclusion
What is a startup ecosystem?
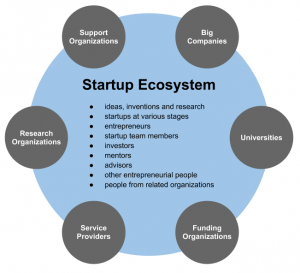
Source: https://www.startupcommons.org/what-is-startup-ecosystem.html
First of all, a startup ecosystem consists of the following main parts:
- Big companies
- Corporations like Samsung, Softbank (Vision Fund) or WeWork (itself a startup) usually have either incubators / accelerators or VCs (e.g. Google Ventures) that help startups.
- Universities
- Most universities in Korea have some kind of program to grow startups. Dongguk University is one of them: “Since 2011, when it was selected first for the Startup Leadership University Cultivation Project, Dongguk University has been named a startup leadership university for eight consecutive years.”
- Funding organizations
- Pay to play! In Korea, startups can get money from government, VCs (e.g. Kakao’s K-Cube Ventures) and accelerators. However, you could argue that VCs nowadays are not funding companies that solve the most urgent problem, climate change. Dropbox ($DBX), Uber ($UBER) and Slack ($WORK) may have had successful exits for their investors / employees, their stock market values after their IPOs are nothing compared to plant based meat company Beyond Meat ($BYND) that is up more than 550% since its IPO.
- Service providers
- You could say that services like AWS (cloud hosting) that have gradually become cheaper has fueled the startup boom. Other services that you need are: legal, financial services etc.
- Research organizations
- The US army (DARPA) and PARC (Xerox) had a big impact on the history of Silicon Valley. Google benefited from NSA and CIA research grants and it is very likely that Facebook has connections to DARPA.
- Support organizations
- Examples: incubators, accelerators, co-working spaces etc.
Minor parts are:
- Ideas, inventions and research
- Startups at various stages
- Entrepreneurs
- Startup team members
- Investors
- Mentors
- Advisers
- Other entrepreneurial people
- People from related organizations
Below is an infographic of the Korean startup ecosystem by Startup Alliance.
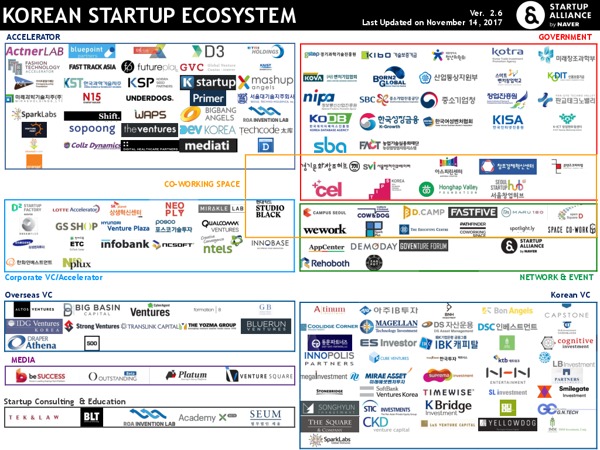
There are more infographics and maps on the website of Startup Alliance.
Incubation centers / accelerators in Seoul and Pangyo
The most famous accelerator in the world is Y Combinator (it is harder to get into Y Combinator than Harvard). Some of its graduates include Airbnb, Stripe, Coinbase, Reddit, Twitch and Memebox. There is a book about them and they have their own podcasts. The differences between an incubation center and accelerator are:
| Incubator | Accelerator | |
| Seed money | Yes | Yes |
| Focus | Innovate | Scale |
| Timeframe | Longer | Shorter |
| Vertical | Yes, likely | Probably not |
| Co-working | Yes, likely | Probably not |
| Owner | Independent | Company |
| Sell equity | Probably not | Yes, likely |
Below is a list of the most famous incubation centers / accelerators in Seoul. Some of the websites are in Korean. A few of the organizations below require foreigners in their team.
- Top accelerators according to Crunchbase:
- Other incubators / accelerators:
- Seoul Global Startup Center
- K-Startup Grand Challenge
- Seoul Global Center
- Campus Seoul
- 500 Startups
- Seoul Startup Hub
- Born2Global
- D.Camp
- Maru180
- WeWork Creator Awards
- WeWork Labs
- Honghap Valley
- Startup Grind Seoul
- TIPS
- N15
- Hyundai Card Studio Black
- Naver D2 Startup Factory
- MY WORKSPACE 3
- Rehoboth
- Seoul IoT
Note: most universities have incubator programs, but they are not listed here.
Co-working spaces in Seoul
Below is a list of the most well known co-working spaces in Seoul.
- WeWork
- Hive Arena
- CCEI
- Startup Alliance Korea
- SparkPlus
- Fast Five
- Cow & Dog
- Idea Factory
- Heyground
- Fab Lab
- Spaces
- Garage
- Space Noah
- Peachtree
- I Startup U
- Tips Town
There are many more! Find them here: https://www.coworker.com/south-korea/seoul.
Korean startup jobs
Working at a startup can be quite good for your career. Often you can learn about many aspects of working life. Rarely do startups need specialists who have only one role. You may even get equity! How to get one? Check the sites below! You can also read about the latest news. For some sites you need to be able to read Korean.
- Angel.co
- F6s
- Seoul Startups (Slack channel)
- RocketPunch
- Demoday
- Jobfindr
Korean unicorns
Rather work at an established Korean startup? Below is a list of Korean startups valued more than one billion US dollar. Source: CBInsights
| Unicorn | Valuation (B$) | Category | Investors |
| Coupang | $9 | eCommerce / Marketplace | Sequoia Capital, Founder Collective, Wellington Management |
| Bluehole* | $5 | Travel Tech (sic) | Tencent Holdings, Stonebridge Capital, IMM Investment |
| Yello Mobile | $4 | Mobile Software & Services | Formation 8 |
| Woowa Brothers* | $2.6 | On Demand | Hillhouse Capital Management, Altos Ventures, Sequoia Capital |
| L&P Cosmetic | $1.78 | Beauty & grooming | CDIB Capital |
| We make price | $1.33 | eCommerce / Marketplace | IMM Investment, NXC |
| Viva Republica (Toss) | $1.2 | Fintech | Bessemer Venture Partners, Qualcomm Ventures, Kleiner Perkins Caufield & Byers |
| Yanolja | $1 | Travel Tech | SBI Investment Korea, Partners Investment, GIC |
* Bluehole is the company behind PlayerUnknown’s game Battlegrounds.
* Woowa Brothers is the company behind food delivery app Baedal Minjok.
Korean technology and innovation
One of the reasons why the Korean government is supporting startups is to get a technological advantage. The Fourth Industrial Revolution, artificial intelligence (AI), fintech, AR/VR, robotics, the Internet of Things (IoT), 3D printing, genetic engineering, quantum computing and other technologies are quickly becoming a part of our daily lives. Korea’s Internet is among the world’s fastest, the mobile shopping rate in Korea is already the highest in the world and the world’s first 5G networks have come online.
Conclusion
Startup life may be attractive, but watch out: there is a saying that 95% of startups fail. There is no substantial data to support that, but the success rate of small businesses is 25% (after 15 years). According to another study, “bit more than half of all startups actually survive to their fourth year, while the startup failure rate at four years is about 44 percent.”

What is the main reason for startups to fail? According to CB Insights there is “no market need” (42%). That means that customers are not interested in the product that the startups offers. A good example is Segway. Great product, but no market demand. The most important thing for any company is to solve a problem. You may think that Airbnb is a high tech company, they started out simply by offering air beds at festivals. This HBR podcast says that startups should first get customers (and figure out their wants and needs) before scaling. Another misconception: startup founders do not have to be young. People like Steve Jobs, Bill Gates and Mark Zuckerberg are extreme outliers: “the average age of entrepreneurs who founded high-growth companies is 45”.


Do you have to be a computer or IT major to do well in such technology focused businesses? Are there free or affordable startup courses for foreigners in Korea?
Hi Sam! Even though the majority of startup founders are engineers, there are non technical founders. They would focus mainly on getting customers / funding and doing all the necessary paperwork. So that the engineers only have to focus on coding. There is a startup school run by the Seoul Global Center: http://global.seoul.go.kr/user.do?menu_id=0310000000&site_code=0101.
WeWork has an accelerator/founder program called WeWork Labs, We have 4 WeWork Labs locations in Seoul. Let me know if you want to know more.
Hi Jason, that is very interesting. Added Labs and sent a contact form!